
C1.1 How has the earth's atmosphere changed over time, and why?.C6.1.1 recall that acids react with some metals and with carbonates and write equations predicting products from given reactants.C6.1 What useful products can be made from acids?.C3.3f recall that carbonates and some metals react with acids and write balanced equations predicting products from given reactants.3.12 Describe the chemical test for: hydrogen, carbon dioxide (using limewater).3.11 Explain the general reactions of aqueous solutions of acids with: metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides, metal carbonates to produce salts.Recall that acids react with some metals and with carbonates, and write equations predicting products from given reactants.
 The test for hydrogen uses a burning splint held at the open end of a test tube of the gas. Knowledge of reactions limited to those of magnesium, zinc and iron with hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. Acids react with some metals to produce salts and hydrogen. Students should be able to describe the difference compared with Group 1 in melting points, densities, strength, hardness and reactivity with oxygen, water and halogens. The transition elements are metals with similar properties which are different from those of the elements in Group 1. 4.1.3.1 Comparison with Group 1 elements. 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. Classification of the first twenty elements in the periodic table on the basis of the number of outer electrons. Answer: Cesium is the most reactive element since it is the second from the bottom of this group, has six electron shells, and exhibits.
The test for hydrogen uses a burning splint held at the open end of a test tube of the gas. Knowledge of reactions limited to those of magnesium, zinc and iron with hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. Acids react with some metals to produce salts and hydrogen. Students should be able to describe the difference compared with Group 1 in melting points, densities, strength, hardness and reactivity with oxygen, water and halogens. The transition elements are metals with similar properties which are different from those of the elements in Group 1. 4.1.3.1 Comparison with Group 1 elements. 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. Classification of the first twenty elements in the periodic table on the basis of the number of outer electrons. Answer: Cesium is the most reactive element since it is the second from the bottom of this group, has six electron shells, and exhibits. 
Brief statement of the principal resemblances of elements within each main group, in particular alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens and noble gases.Investigate reactions between acids and bases use indicators and the pH scale Calcium + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + hydrogen.Magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen.Write formula equations for these reactions.Write word equations for these reactions.Which is the more reactive, magnesium or calcium?.The Group 1 metals get more reactive the lower they are in the group. Group 1 is the most reactive group of metals. Remind students about the test for hydrogen.Ĭalcium can be distributed on pieces of filter paper.
#REACTIVITY TABLE OF ELEMENTS HOW TO#
When the pressure can be felt, take your thumb off and test the gas with a lighted splint.ĭiscussion about how to judge the speed of the reaction is advisable. Drop another bit of magnesium into the first test-tube and put your thumb over the end. Compare the reactivity of the two metals. Into the other, drop a small piece of calcium. Into one test-tube drop a small piece of magnesium. Fill two test-tubes a quarter with dilute hydrochloric acid. Calcium is water reactive, see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC019c. Magnesium is pyrophoric and water reactive, see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC059b. Hydrochloric acid is of low hazard, see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC047a. Read our standard health and safety guidance. Students will be able to discover that group 1 metals are more reactive than group 2 RSC Yusuf Hamied Inspirational Science Programme. Introductory maths for higher education. The physics of restoration and conservation. Magnesium is the eighth most abundant element in the Earth’s crust, and calcium is the fifth. Calcium is found in chalk, limestone, gypsum and anhydrite. The main minerals in which magnesium is found are carnellite, magnesite and dolomite. Instead, they are widely distributed in rock structures. 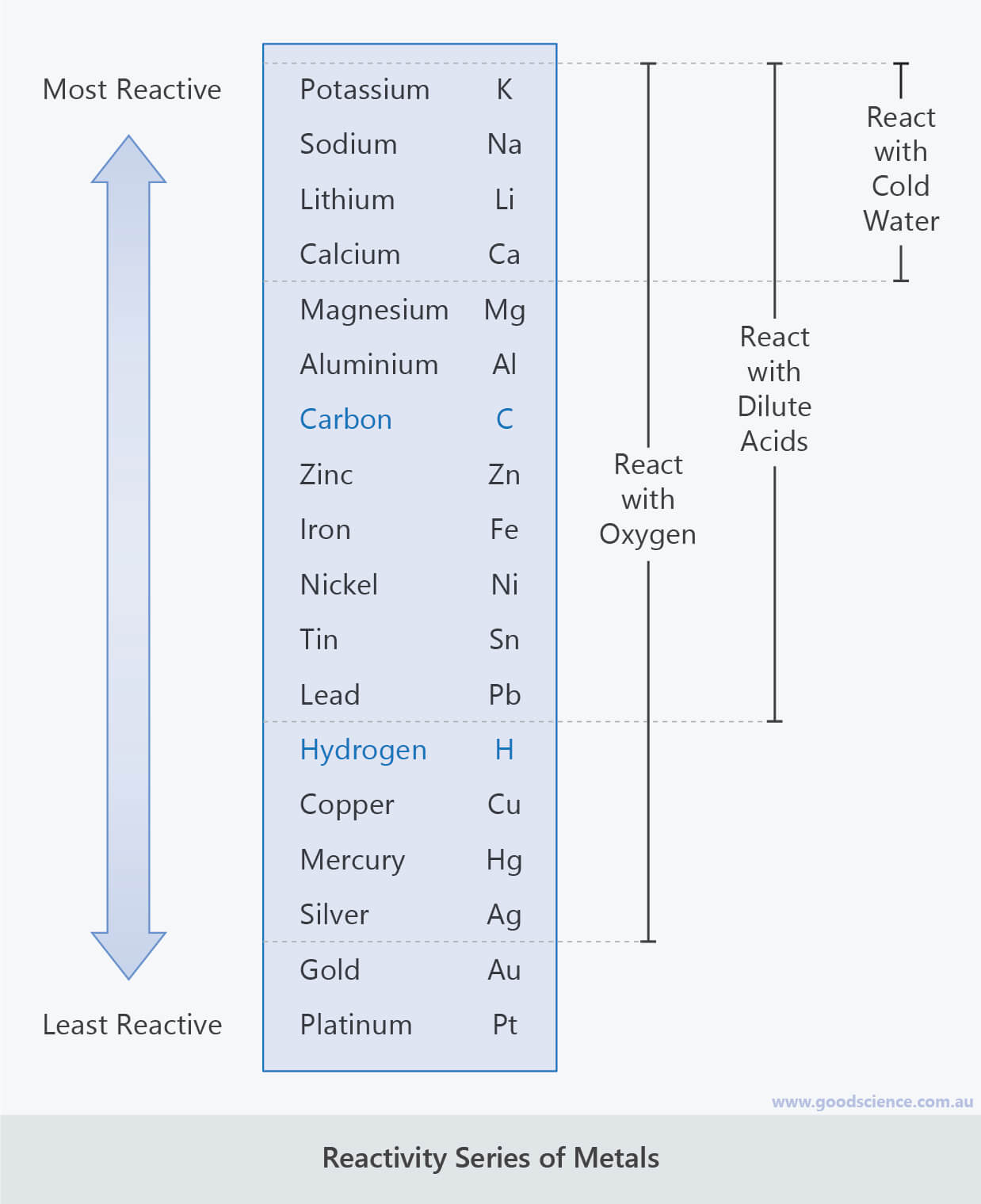
These elements are all found in the Earth’s crust, but not in the elemental form as they are so reactive.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
